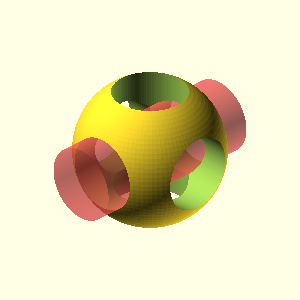OpenSCAD Code Blocks in Org mode
Org Mode support for OpenSCAD
Introduction
OpenSCAD is a solid 3D CAD modeler that uses a scripting language to create 3D models. Its programmatic nature makes it particularly well-suited for integration with Org mode through Babel source code blocks. This integration allows you to:
- Embed 3D model definitions directly within your Org documents
- Generate and preview models without leaving your editing environment
- Capture OpenSCAD console output for debugging and documentation
- Create parameterized designs using Org mode variables
- Maintain complete design documentation alongside the CAD code
- Export models in various formats (images or cad files) for visualization or use in other applications
Unlike interactive CAD tools, OpenSCAD focuses on precision and parametric design, making it ideal for technical parts, mathematical models, and 3D-printable objects. When combined with Org mode, it becomes a powerful tool for creating reproducible, well-documented CAD workflows.
Requirements and Setup
Installing OpenSCAD
To use OpenSCAD source blocks in Org mode, you must first have the OpenSCAD program itself installed on your system.
Official installers, packages, and detailed instructions are available for all major operating systems on the OpenSCAD downloads page.
- Linux: Available in most distribution repositories (e.g.,
sudo apt install openscad). - macOS: Available via Homebrew (
brew install openscad) or direct download. - Windows: Available via WinGet (
winget install -e OpenSCAD.OpenSCAD) or direct download.
Installing scad-mode in Emacs
Emacs Configuration
Add OpenSCAD support to your Babel languages:
(org-babel-do-load-languages
'org-babel-load-languages
'((scad . t)))
;; Optional: Set OpenSCAD executable path if not in system PATH
(setq org-babel-openscad-command "openscad")
Org Mode Features for OpenSCAD Source Code Blocks
Header Arguments
OpenSCAD code blocks support several header arguments that map to OpenSCAD command-line options and rendering parameters:
Core Babel Headers
:results- Defaults tofilewhen the:fileheader is specified:exports- Control what gets exported (code, results, both, none):file- Required for generating any output (image or model file):cmdline- Additional command-line arguments for OpenSCAD:var- Pass variables from other code blocks to parameterize designs
OpenSCAD-Specific Rendering Headers
:colorscheme- Color scheme for rendering (e.g.,Cornfield,Sunset,Metallic,Starnight):projection- Projection type:ortho(orthographic) orperspective:camera- Camera position and orientation astransx,transy,transz,rotx,roty,rotz,dist:view- View mode:axes,scales,edges, orplain(no overlays):size- Render size aswidth,heightin pixels (e.g.,300,300):imgsize- Alternative size parameterwidth,height
Sessions
OpenSCAD does not support persistent sessions in the traditional Babel sense, as each code block execution starts a new OpenSCAD process. However, you can use Org mode variables to maintain parameter consistency across blocks.
Result Types
OpenSCAD produces model files (STL, OFF, AMF, 3MF, CSG), 2D export files (DXF, SVG), and image files (PNG) via the :file header argument. Debug output formats (AST, TERM, NEF3, NEFDBG) are also supported.
Differences from Other Supported Languages
Console output from OpenSCAD's echo() function, warnings, and errors is not directly captured by Babel. To capture this output, use the shell wrapper method described in the console section.
Examples of Use
Basic 3D Model Generation
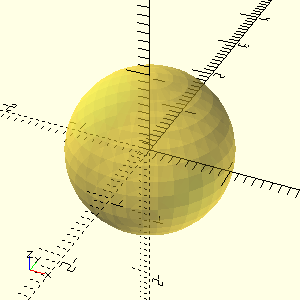
Create a simple cube and export it as a PNG image:
#+NAME: basic-sphere
#+CAPTION: A simple sphere generated with OpenSCAD
#+HEADER: :file ./images/basic-sphere.png
#+HEADER: :colorscheme Cornfield
#+HEADER: :size 300,300
#+begin_src scad :exports results
diameter = 10;
color("Cornfield", 0.5) sphere(s=diameter, $fn=36);
#+end_src
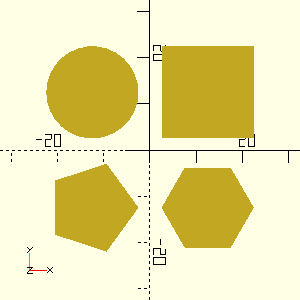
Primitive 2D shapes
When working with 2D geometries in OpenSCAD, using orthographic projection with a top-down camera view provides an accurate, undistorted representation of dimensions. This is particularly important for 2D shapes where precise measurements matter.
#+NAME: square-circle
#+CAPTION: Some 2D primitives
#+HEADER: :file ./images/some-2d-primitives.png
#+HEADER: :colorscheme Cornfield
#+HEADER: :projection ortho
#+HEADER: :camera 0,0,0,0,0,0,0
#+HEADER: :size 300,300
#+begin_src scad :exports both
side=20; radius=10; offset=12.5;
module place_in_quadrant(quadrant) {
x = (quadrant==1 || quadrant==4 ? 1 : -1) * offset;
y = (quadrant==1 || quadrant==2 ? 1 : -1) * offset;
translate([x, y]) children(0);
}
place_in_quadrant(1) square(side, center=true);
place_in_quadrant(2) circle(radius, $fn=30);
place_in_quadrant(3) circle(radius, $fn=5);
place_in_quadrant(4) circle(radius, $fn=6);
#+end_src
The :camera header supports two different camera modes in OpenSCAD, each with its own parameter format:
- Gimbal Camera uses the format:
transx,transy,transz,rotx,roty,rotz,distance, where:transx,transy,transz- Translation (movement) of the object in X, Y, Z directionsrotx,roty,rotz- Rotation around X, Y, Z axes in degreesdistance- Distance between camera and object center
- Vector Camera uses the format:
eyex,eyey,eyez,centerx,centery,centerz, where:eyex,eyey,eyez- Eye (camera) position coordinatescenterx,centery,centerz- Center (target) position coordinates
Organizing Code with Noweb References
Org mode's noweb syntax allows you to break complex designs into reusable components and share parameters across multiple code blocks.
Define a Reusable Module
Store the box geometry as a reusable module:
#+NAME: box-module
#+begin_src scad :exports code :results none
module box(w, l, h, t) {
difference() {
cube([w, l, h], center=true);
translate([0, 0, t])
cube([w-2*t, l-2*t, h], center=true);
}
}
#+end_src
Define Shared Parameters
Store design parameters in a separate block for easy modification:
#+NAME: box-params #+begin_src scad :exports code :results none width = 30; length = 20; height = 10; thickness = 2; #+end_src
Combine Components with Noweb
Use <<block-name>> syntax to include code from other blocks:
#+NAME: parametric-box
#+CAPTION: Combining modules and parameters with noweb references
#+HEADER: :file ./images/parametric-box.png
#+HEADER: :colorscheme Cornfield
#+HEADER: :projection ortho
#+HEADER: :size 300,300
#+begin_src scad :exports both :noweb yes
<<box-module>>
<<box-params>>
// Build the box
box(width, length, height, thickness);
// These echos will NOT appear in results
echo("width, length, height, thickness: ", width, length, height, thickness);
echo(version=version());
#+end_src
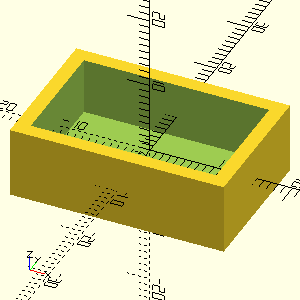
The echo() statements are processed by OpenSCAD but not captured by org-babel.
capturing OpenSCAD Console Output
Unlike some babel languages, OpenSCAD does not directly support console output capture through the :results output header argument. However, you can capture OpenSCAD's console output (including echo() statements) by wrapping the OpenSCAD execution in a shell code block.
Capturing All Console Output Types
#+NAME: parametric-box-full-output #+CAPTION: Complete output including debug messages and render statistics #+begin_src shell :results output :exports both :noweb yes :wrap results output=$(openscad -o /dev/null --export-format asciistl - <<'EOF' 2>&1 <<parametric-box>> EOF ) echo "=== Debug Information ===" echo "$output" | grep -i echo echo echo "=== Render Statistics ===" echo "$output" | grep -v -i echo #+end_src
#+RESULTS: parametric-box-full-output #+begin_results === Debug Information === ECHO: "width, length, height, thickness: ", 30, 20, 10, 2 ECHO: version = [2021, 1, 0] === Render Statistics === Geometries in cache: 3 Geometry cache size in bytes: 2184 CGAL Polyhedrons in cache: 1 CGAL cache size in bytes: 23888 Total rendering time: 0:00:00.018 Top level object is a 3D object: Simple: yes Vertices: 16 Halfedges: 48 Edges: 24 Halffacets: 22 Facets: 11 Volumes: 2 #+end_results
Explanation
- The shell code block uses
openscad -o /dev/nullto discard the.stloutput --export-format asciistlensures OpenSCAD processes the file2>&1redirects both stdout and stderr to capture all outputecho()statements in OpenSCAD are captured as "ECHO:" lines- The exit code shows whether the OpenSCAD code compiled successfully
OpenSCAD Title Logo
This example demonstrates how to generate an image using an OpenSCAD code block and place the resulting image anywhere in your Org document using the #+RESULTS: directive. In this case, the logo is generated and displayed at the top of the page as the title logo.
#+NAME: OpenSCAD logo
#+CAPTION: OpenSCAD logo
#+HEADER: :file ./images/openscad-logo.png
#+HEADER: :colorscheme Cornfield
#+HEADER: :projection ortho
#+HEADER: :camera 0,0,0,60,0,45,0
#+HEADER: :view none
#+HEADER: :size 300,300
#+begin_src scad :export results :result output
Logo();
module Logo(size=50, $fn=100) {
hole = size/2;
cylinderHeight = size * 1.25;
difference() {
sphere(d=size);
cylinder(d=hole, h=cylinderHeight, center=true);
#rotate([90, 0, 0]) cylinder(d=hole, h=cylinderHeight, center=true);
rotate([0, 90, 0]) cylinder(d=hole, h=cylinderHeight, center=true);
}
}
#+end_src
#+RESULTS: OpenSCAD logo [[file:./images/openscad-logo.png]]
See the OpenSCAD banner at the top of the page, generated by the code block above. View the original source code.
Troubleshooting
OpenSCAD Not Found
If you encounter errors like openscad: command not found, ensure OpenSCAD is installed and the path is set correctly in your Emacs Configuration using the org-babel-openscad-command variable.
Syntax Errors
OpenSCAD is strict about syntax. Use the console output capture method to debug errors (see console section).
Performance Issues
Complex models may render slowly. Simplify designs, reduce $fn values, or use smaller :size values (e.g., :size 200,200) for faster previews.